一、模式结构与核心角色
意图:在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态,以便在以后恢复它。
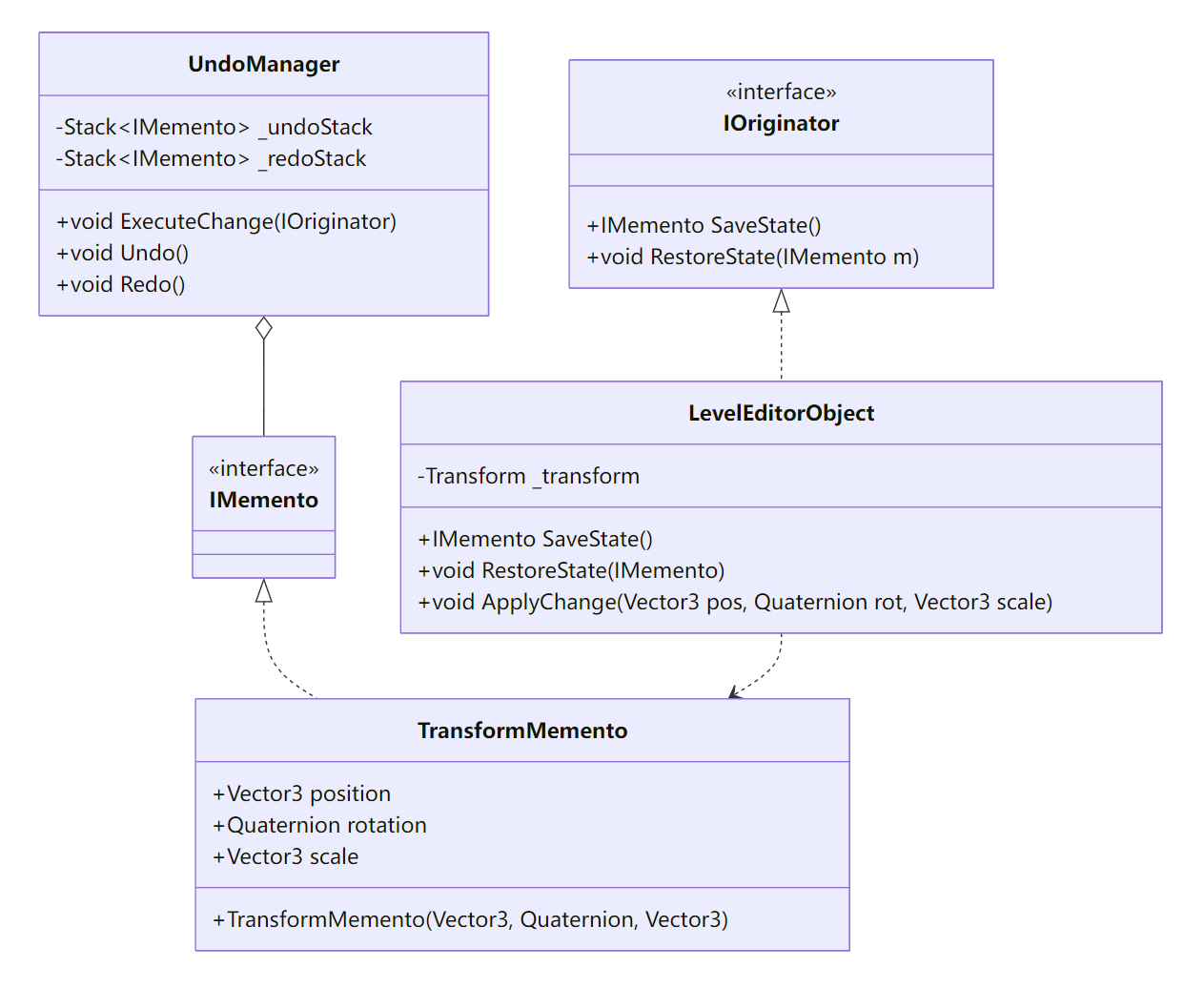
Originator(发起者)
拥有要保存状态的对象,提供SaveState()和RestoreState(memento)方法。Memento(备忘录)
存储 Originator 的内部状态,通常对外只暴露给 Originator;对 Caretaker 保持透明。Caretaker(管理者)
持有一系列 Memento(如栈或队列),并根据需求保存、检索,不修改 Memento 内容。
二、Unity 实战:关卡编辑器的撤销/重做系统
2.1 定义 Memento 接口与具体实现
/// <summary>标记备忘录类型,无需暴露内部结构</summary>
public interface IMemento { }
/// <summary>存储 Transform 状态的备忘录</summary>
public class TransformMemento : IMemento {
public readonly Vector3 Position;
public readonly Quaternion Rotation;
public readonly Vector3 Scale;
public TransformMemento(Vector3 pos, Quaternion rot, Vector3 scale) {
Position = pos;
Rotation = rot;
Scale = scale;
}
}
2.2 Originator:可编辑对象
public class LevelEditorObject : MonoBehaviour, IOriginator {
private Transform _t;
void Awake() {
_t = transform;
}
/// <summary>创建当前状态的备忘录</summary>
public IMemento SaveState() {
return new TransformMemento(_t.localPosition, _t.localRotation, _t.localScale);
}
/// <summary>根据备忘录恢复状态</summary>
public void RestoreState(IMemento m) {
var tm = m as TransformMemento;
if (tm == null) return;
_t.localPosition = tm.Position;
_t.localRotation = tm.Rotation;
_t.localScale = tm.Scale;
}
/// <summary>示例:应用一次变换并记录快照</summary>
public void ApplyChange(Vector3 pos, Quaternion rot, Vector3 scale) {
_t.localPosition = pos;
_t.localRotation = rot;
_t.localScale = scale;
}
}
2.3 Caretaker:撤销管理器
public class UndoManager : MonoBehaviour {
private readonly Stack<(IOriginator origin, IMemento memento)> _undoStack = new();
private readonly Stack<(IOriginator origin, IMemento memento)> _redoStack = new();
/// <summary>执行一次变更前记录状态</summary>
public void ExecuteChange(IOriginator origin) {
// 清空 redo 栈
_redoStack.Clear();
// 保存变更前状态
var snapshot = origin.SaveState();
_undoStack.Push((origin, snapshot));
}
/// <summary>撤销上一次变更</summary>
public void Undo() {
if (_undoStack.Count == 0) return;
var (origin, memento) = _undoStack.Pop();
// 记录当前状态以便重做
_redoStack.Push((origin, origin.SaveState()));
// 恢复
origin.RestoreState(memento);
}
/// <summary>重做上一次撤销</summary>
public void Redo() {
if (_redoStack.Count == 0) return;
var (origin, memento) = _redoStack.Pop();
_undoStack.Push((origin, origin.SaveState()));
origin.RestoreState(memento);
}
}
2.4 客户端组合:操作流程
public class LevelEditorController : MonoBehaviour {
public UndoManager undoManager;
private LevelEditorObject selected;
void Update() {
// 选中对象并移动示例
if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0)) {
// 选中
selected = RaycastSelect();
}
if (selected != null && Input.GetMouseButton(0)) {
// 在变换前记录状态
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Space)) {
undoManager.ExecuteChange(selected);
}
// 应用变换
var newPos = selected.transform.localPosition + Vector3.right * Time.deltaTime;
selected.ApplyChange(newPos, selected.transform.localRotation, selected.transform.localScale);
}
// 撤销/重做
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Z)) undoManager.Undo();
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Y)) undoManager.Redo();
}
private LevelEditorObject RaycastSelect() {
if (Physics.Raycast(Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition), out var hit)) {
return hit.collider.GetComponent<LevelEditorObject>();
}
return null;
}
}
三、进阶话题
3.1 复合 Memento
- 多对象同时快照
为一组 Originator 创建 CompositeMemento,将多个单体 Memento 聚合,支持跨对象的事务性 Undo:
public class CompositeMemento : IMemento {
public readonly List<IMemento> Snapshots;
public CompositeMemento(IEnumerable<IMemento> snaps) {
Snapshots = new List<IMemento>(snaps);
}
}
3.2 差异化快照(Delta Memento)
存储变更差值 而非完整状态,节省内存:
$$\Delta_{\text{pos}} = \text{newPos} - \text{oldPos},\quad\Delta_{\text{rot}} =\text{newRot} * \text{oldRot}^{-1}$$恢复时应用差值,适用于大批量小变动场景。
3.3 持久化存档
- 将 Memento 序列化为 JSON 或二进制,写入磁盘,实现游戏存档/读取:
string json = JsonUtility.ToJson(memento);
File.WriteAllText(path, json);
// 读取
var m = JsonUtility.FromJson<TransformMemento>(json);
origin.RestoreState(m);
3.4 内存与性能
- 历史深度控制:限制
_undoStack大小,防止内存膨胀; - 快照压缩:周期性合并多次快照,仅保留关键检查点;
- 浅拷贝 vs 深拷贝:对于复杂对象,需确保状态拷贝全面,避免残留引用。
四、常见陷阱与防坑指南
| 场景 | 陷阱 | 建议 |
|---|---|---|
| 未保存全部字段 | Memento 只保存部分状态,Restore 后对象进入不一致状态 | 明确 Snapshot 范围,保存所有会影响行为的字段 |
| 引用类型浅拷贝 | Memento 中保存的引用仍指向原对象,后续变更影响快照 | 对引用字段进行深度克隆,或仅保存不可变标识并延迟获取 |
| 堆栈无限增长 | 长时间编辑后 Undo 历史过多,内存占用剧增 | 限制栈深度,或周期性清理最旧记录 |
| 恢复顺序依赖 | 多对象快照互相依赖,但恢复顺序不当导致状态错乱 | 使用 CompositeMemento 原子恢复所有对象状态,保证事务一致性 |
| 跨场景 Memento 失效 | 快照中引用的 GameObject 场景卸载后再恢复会找不到对象 | 在存档时保存对象唯一标识符(如 GUID)并在恢复后重新映射 GameObject |
五、小结与最佳实践
- 封装与透明:Originator 负责状态捕获与恢复,Caretaker 只持有 Memento,不窥视其内部;
- 快照策略:根据场景选择完整快照、差值快照或事务性复合快照;
- 资源管理:对历史记录栈做深度限制与清理,防止内存爆炸;
- 序列化支持:结合 JsonUtility、BinaryFormatter 或自定义序列化,实现跨会话持久化;
- 测试覆盖:为每种 Memento 类型编写单元测试,确保 RestoreState 完整恢复。
